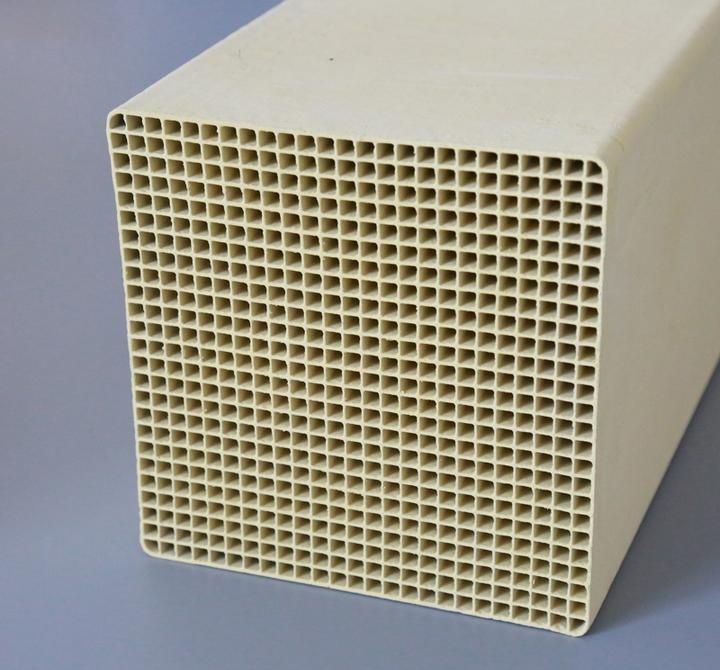
What are the advantages compared to bag filter dust collectors?
(1) Superior High-Temperature Resistance.
Ceramic filter can operate within a temperature range of 200–900°C, with short-term peak tolerance up to 1100°C. In contrast, baghouse dust collectors are typically limited to 120–180°C, making ceramic filter ideal for high-temperature industrial processes without requiring cooling systems.
(2) Ultra-Low Emission Performance
Featuring a surface dense layer with >80% porosity and multi-layer superimposed pore structures ranging from 25–45 nm, ceramic filter achieve >99.99% PM2.5 capture efficiency. This ensures stable emission concentrations below 5 mg/Nm³, exceeding most regulatory standards .
(3) Extended Service Life
Ceramic fiber filter offer a service life of over 5 years, significantly outperforming baghouse filters, which often require annual replacement. This reduces downtime and long-term maintenance costs
(4) Energy-Efficient Operation
Thanks to their high-temperature adaptability, ceramic filter eliminate the need for cooling systems. Additionally, their low-pressure drop design minimizes pulse-jet cleaning frequency, cutting energy consumption.
(5) Maintenance-Free
Ceramic filters are immune to common baghouse issues such as filter bag abrasion, clogging, or moisture-related failures. They support online compartment-based maintenance, allowing continuous operation without shutdowns.
6) Compatibility with Waste Heat Recovery
With a minimal temperature drop (20–50°C) across the system, ceramic filters enable efficient waste heat recovery downstream, contributing to overall energy savings and sustainability.
What are the advantages compared to SCR catalysts?
(1) Integration: From Single-Function Denitrification to Multi-Pollutant Synergistic Control
The core function of SCR catalysts is selective catalytic reduction for denitrification, targeting only NOₓ. This typically requires a multi-step process involving baghouse dust collectors and desulfurization units in series (e.g., "desulfurization → dust removal → denitrification") . In contrast, ceramic filters integrate dust removal, denitrification, and desulfurization into a single system. This integrated design fundamentally transforms the traditional SCR approach of "single function, multiple equipment in series," significantly simplifying the process flow and reducing footprint
(2) Anti-Poisoning: From Prone to Deactivation to Long-Term Stable Operation
SCR catalysts are highly susceptible to poisoning and deactivation. Dust in high-temperature flue gas (e.g., alkali metals, arsenic, selenium) can physically cover active sites, reducing denitrification efficiency. SO₂ oxidation products can irreversibly react with active components to form sulfates, and ammonium bisulfate formed from NH₃ and SO₃ can clog catalyst pores . Ceramic filters address these issues through structural barriers and material modifications:
Dust Blocking: The "surface dense layer + internal porous structure" of ceramic filters intercepts dust on the outer surface, preventing it from reaching the internal catalytic layer. This extends catalyst life to over 5 years (compared to 1–2 years for traditional SCR catalysts), significantly reducing replacement costs and downtime.
(3) High-Density Active Sites and Superior Reaction Efficiency
The denitrification efficiency of ceramic filters benefits from highly dispersed and densely loaded catalytic active components. Catalysts are embedded within ceramic fibers or internal pores, with deep impregnation penetrating the entire 20 mm tube wall to form an active catalytic layer . This design increases the contact area between active sites and NOₓ/NH₃ by tens of times compared to traditional honeycomb SCR catalysts. The gas residence time within the filter tube is extended by 2–3 times, enabling a denitrification efficiency exceeding 95%
What other functions do ceramic filter have besides denitrification and dust removal?
(1) Integrated Acid Gas Removal: Simultaneous Removal of SO₂, HF, and HCl
By integrating desulfurization agents (e.g., baking soda or lime powder), ceramic filters enable highly efficient, coordinated removal of acidic gases through a dry acid removal process. The dust cake layer trapped on the filter's outer surface contains unreacted alkaline solids, which further react with SO₂, HF, and other acidic pollutants, significantly improving removal efficiency
(2) Dioxin Destruction: Catalytic Decomposition Exceeding 99% Efficiency
Equipped with a vanadium-based catalyst, ceramic filters can decompose dioxins by reacting with oxygen, breaking them down into non-toxic substances such as CO₂, H₂O, and HCl. This catalytic destruction mechanism achieves a removal efficiency of over 99% without generating secondary pollution risks
(3) Synergistic Effects: Unifying Multiple Pollutants into One Streamlined System
The "integrated" design of ceramic filters allows for the synergistic removal of acid gases, dioxins, NOx, and particulate matter in a single system. This approach delivers a "1+1>2" synergistic effect, resulting in lower investment costs, a smaller footprint, higher removal efficiency, greater system reliability, and simpler operation compared to traditional multi-step processes
Key Parameters for Ceramic Filter
(1) Material Quality
Materials with low impurity content and a low slag ball ratio are preferable. The specific surface area (often referred to as bic value) should ideally be around 200±40 m²/g, indicating a structure conducive to efficient filtration and catalyst loading.
(2) Forming Process
Determine the molding method. External mold forming leaves the original mold imprint on the outer surface, which can enhance the adsorption of desulfurization agents and prevent particles from penetrating the tube layer, reducing clogging. Internal mold forming often requires surface grinding and may result in a product with a "larger head and smaller tail" dimensional inconsistency.
(3) Mechanical Strength
Verify the structural integrity. The C-ring strength at all points of the entire ring should exceed 0.4 MPa, not just on average. Inquire if secondary curing and deep grinding processes are employed, as these treatments significantly enhance overall strength and durability.
(4) Workmanship & Precision
Inspect the physical finish. Key indicators include flange flatness, the straightness (bending degree) of the filters, and the uniformity of the tube wall thickness. Superior workmanship in these areas ensures better sealing and more stable performance in the system.
(5) Service & Support
Evaluate the supplier's commitment. Look for clear warranty periods (e.g., 3 or 5 years). A reliable supplier should have in-depth knowledge of on-site processes and offer comprehensive after-sales services, including technical support and maintenance guidance
Is a Ceramic Filter Suitable for Your Working Conditions?
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, as each industrial scenario requires specific analysis. However, there are no extreme conditions that ceramic filter tubes cannot handle. Call us now for a free, customized analysis of your working conditions. We also offer trial ceramic samples to validate performance—ensuring your peace of mind before making any commitment.